Frequently Asked Questions (Arduino)
Below are 20 frequently asked questions about Arduino — 10 of the most commonly searched questions plus 10 other commonly asked/practical topics. Each question has a short, practical answer and links where relevant.
Table of contents
- Frequently Asked Questions (Arduino)
- Table of contents
- 1. What is an Arduino and which board should I buy first? {#1-what-is-an-arduino-and-which-board-should-i-buy-first}
- 2. How do I install the Arduino IDE? {#2-how-do-i-install-the-arduino-ide}
- 3. How do I upload a sketch to my Arduino? {#3-how-do-i-upload-a-sketch-to-my-arduino}
- 4. Why is my Arduino not detected by my computer? {#4-why-is-my-arduino-not-detected-by-my-computer}
- 5. What's the difference between 5V and 3.3V boards? {#5-whats-the-difference-between-5v-and-33v-boards}
- 6. How do I power an Arduino safely from a battery? {#6-how-do-i-power-an-arduino-safely-from-a-battery}
- 7. What is a sketch? {#7-what-is-a-sketch}
- 8. What are digital, analog, and PWM pins? {#8-what-are-digital-analog-and-pwm-pins}
- 9. Why does my circuit reset when I connect a component? {#9-why-does-my-circuit-reset-when-i-connect-a-component}
- 10. How do I use libraries in Arduino sketches? {#10-how-do-i-use-libraries-in-arduino-sketches}
- 11. What's the easiest way to learn electronics for Arduino? {#11-whats-the-easiest-way-to-learn-electronics-for-arduino}
- 12. How do I read a sensor value and display it? {#12-how-do-i-read-a-sensor-value-and-display-it}
- 13. What is debounce and why do I need it for buttons? {#13-what-is-debounce-and-why-do-i-need-it-for-buttons}
- 14. How can I power motors without damaging my Arduino? {#14-how-can-i-power-motors-without-damaging-my-arduino}
- 15. Can I connect multiple Arduinos together? {#15-can-i-connect-multiple-arduinos-together}
- 16. Why does my analogRead return noisy values? {#16-why-does-my-analogRead-return-noisy-values}
- 17. How do I update firmware on newer boards (e.g., ESP32, SAMD)? {#17-how-do-i-update-firmware-on-newer-boards-eg-esp32-samd}
- 18. What are good practices for prototyping vs production? {#18-what-are-good-practices-for-prototyping-vs-production}
- 19. How do I troubleshoot a non-working sketch? {#19-how-do-i-troubleshoot-a-non-working-sketch}
- 20. Can I use Arduino with Python or other languages? {#20-can-i-use-arduino-with-python-or-other-languages}
1. What is an Arduino and which board should I buy first?
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform combining easy-to-use hardware (microcontroller boards) and software (Arduino IDE and libraries). For beginners, the Arduino Uno (or a well-supported compatible) is the safest choice due to extensive documentation and community support.
Official site: https://www.arduino.cc/
2. How do I install the Arduino IDE?
Download the Arduino IDE or use the Arduino CLI from the official Arduino downloads page. Choose your OS installer (Windows/macOS/Linux) and follow the installer steps. On Windows, install the USB driver when prompted or use an admin installer.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/software
3. How do I upload a sketch to my Arduino?
Connect your board with a data-capable USB cable (some cables are power only), open the Arduino IDE, select the correct board model and serial port (Tools → Board / Port), open a sketch, then press Upload. The message 'Done uploading' indicates success. If you can not see the port, then go to the next FAQ number 4.
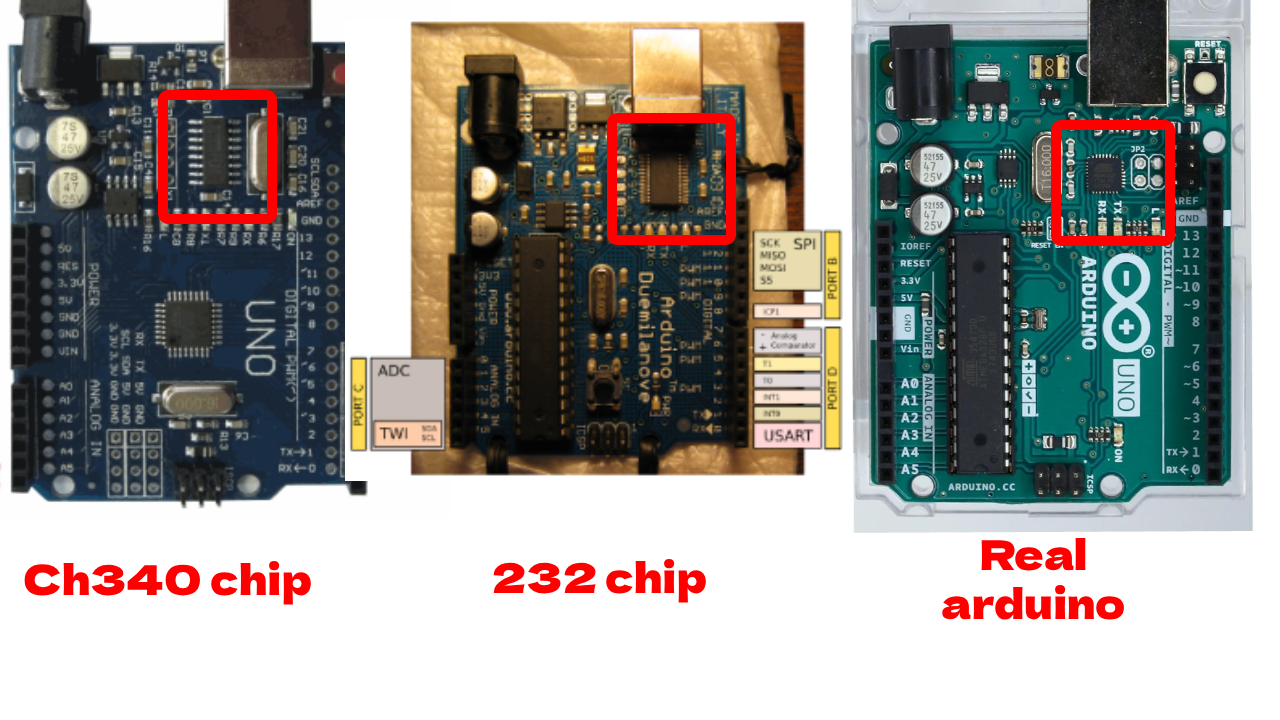
4. Why is my Arduino not detected by my computer?
Common causes:
- Faulty or power-only USB cable (use a data cable)
- Missing USB driver (install from vendor)
- Wrong port selected in the IDE
- Defective USB-to-serial chip on some clones
- Need to install drivers for your clone (arduinos dont need drivers)
Try another cable/port, update drivers, and check Device Manager (Windows) or dmesg/lsusb (Linux/macOS).
5. What's the difference between 5V and 3.3V boards?
5V boards (Arduino Uno, Mega) use 5V logic. Many modern boards (ESP32, some SAMD) use 3.3V logic. Never connect a 5V output directly to a 3.3V input — use a level shifter or voltage divider to avoid damaging components.
6. How do I power an Arduino safely from a battery?
Use a regulated power source. For an Uno, you can supply 7–12V to VIN (onboard regulator) or 5V to the 5V rail if regulated. For portability, USB power banks or a regulated LiPo + voltage regulator are common. Always observe polarity and common ground when connecting external supplies.
7. What is a sketch?
A sketch is an Arduino program, usually written in C/C++. It has two main functions: setup() — runs once, and loop() — repeats continuously. Sketches are compiled and uploaded to the board.
Arduino reference on structure: https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/
8. What are digital, analog, and PWM pins?
- Digital pins: read/write HIGH or LOW (0/1).
- Analog input pins: read variable voltage via ADC (analogRead).
- PWM pins: digital pins that support pulse-width modulation to simulate varying voltage for dimming LEDs or controlling motor speed (analogWrite on some boards).
Arduino I/O reference: https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/analog-io/
9. Why does my circuit reset when I connect a component?
This usually indicates a power issue — the component draws excessive current or there's a short. Check wiring carefully, ensure your power supply can provide required current, add decoupling capacitors, and test components individually. Your last step is, unhook all wires, let it cool for a minute powered down, then see if it's still functioning with the blink example.
10. How do I use libraries in Arduino sketches?
Install libraries via the Arduino IDE's Library Manager (Sketch → Include Library → Manage Libraries) or place them in your sketchbook libraries/ folder. Then include the header with #include <LibraryName.h> and review the library's examples.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/Libraries
11. What's the easiest way to learn electronics for Arduino?
Begin with simple components: LEDs, resistors, buttons, and a breadboard. Follow step-by-step tutorials that explain basic concepts such as Ohm's law, series/parallel circuits, and safe wiring. Hands-on projects teach faster than theory alone.
12. How do I read a sensor value and display it?
Determine whether the sensor outputs analog or digital. Use analogRead() for analog sensors or digitalRead() for digital sensors. Use Serial.print() to view values in the Serial Monitor, or send values to an LCD/OLED display or web dashboard depending on your board.
13. What is debounce and why do I need it for buttons?
Mechanical switches produce noisy transitions when toggled. Debouncing (software delay, state filtering, or hardware RC filtering) prevents multiple triggers from a single press. See the Arduino debounce example for patterns.
Debounce example: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BuiltInExamples/Debounce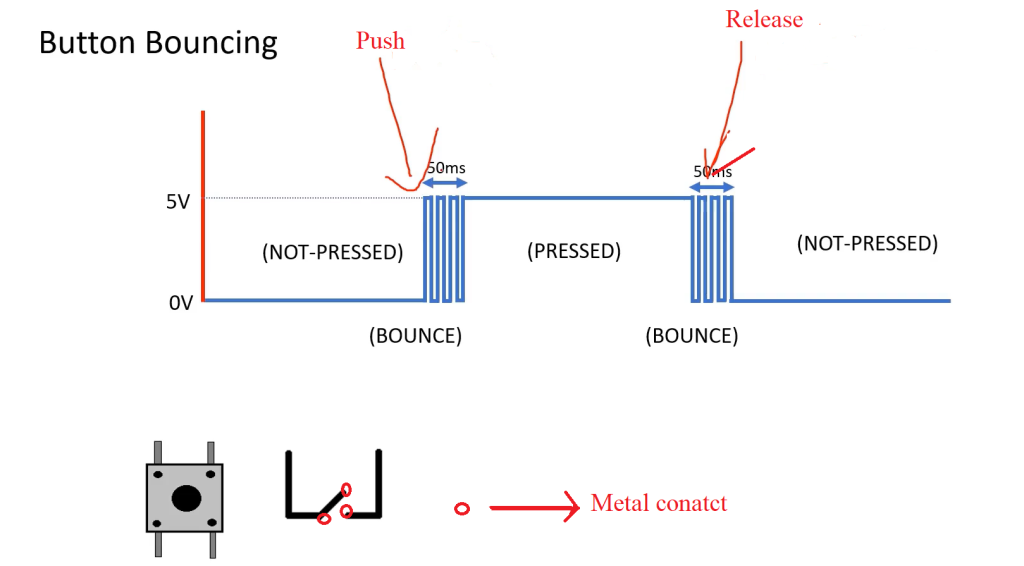 Go to this page for more info on buttons.
Go to this page for more info on buttons.
14. How can I power motors without damaging my Arduino?
Motors draw high current and can generate electrical noise. Use a separate motor power supply, common ground with the Arduino, and motor drivers or H-bridges rated for your motor. Add flyback diodes for DC motors and capacitors for noise suppression.
15. Can I connect multiple Arduinos together?
Yes. You can use serial (UART), I2C, or SPI to communicate between microcontrollers. Decide on a master/slave or peer architecture and handle addressing and clocking carefully. Ensure voltage levels match between boards. 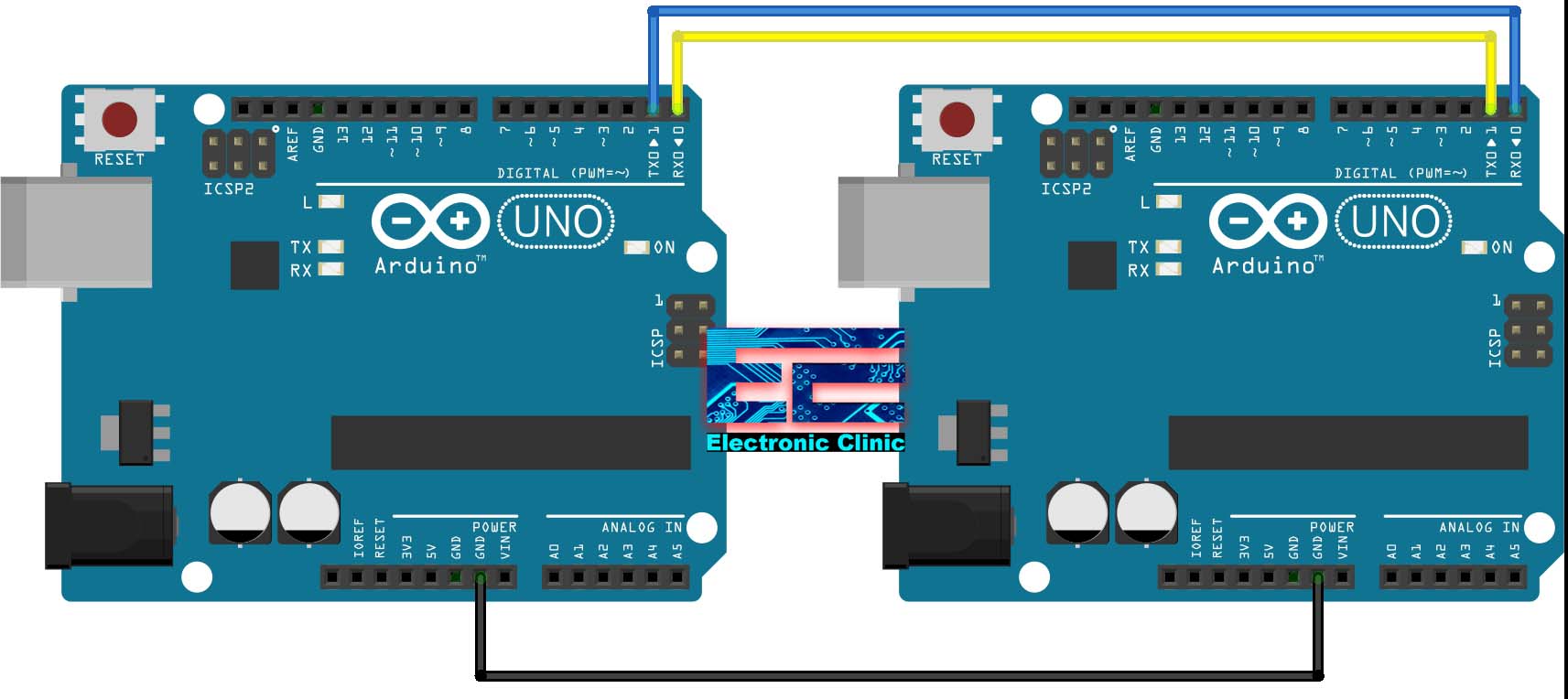
16. Why does my analogRead return noisy values?
Analog values can fluctuate due to electrical noise, poor grounding, or high source impedance. Use averaging (multiple samples), smoothing filters, proper grounding, and keep analog wiring away from high-current traces. 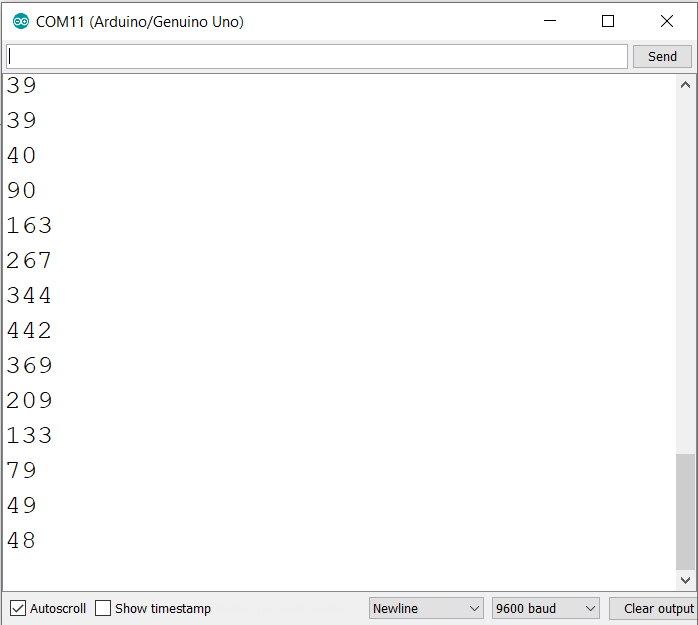
17. How do I update firmware on newer boards (e.g., ESP32, SAMD)?
Many boards can be flashed from the Arduino IDE. Some platforms (ESP) use tools like esptool.py for advanced flashing. Follow the board vendor's flashing instructions, and ensure the correct boot mode or bootloader is used for your board.
18. What are good practices for prototyping vs production?
Prototype on a breadboard or solderless perfboard. When moving to production:
- Move to soldered connections or a PCB
- Use reliable power supplies and connectors
- Add protection components (fuses, TVS diodes) where appropriate
- Consider enclosures and thermal management
 find them here
find them here
19. How do I troubleshoot a non-working sketch?
Use Serial.print() to trace program flow and variable values, isolate hardware by testing components individually, try a known-good example sketch, and simplify your code to the smallest failing case.
20. Can I use Arduino with Python or other languages?
Yes. Standard Arduinos can communicate over serial with Python (using pyserial). Some boards (ESP32, some microcontrollers) can run MicroPython or CircuitPython directly. Use the toolchain that best fits your workflow. NOTE that all of thease option are NOT industry standard, they are limiting, they only work on some MCU's, and genarly not supported.